Introducing Milvus Data Migration Tool
Important Note: The Mivus Data Migration Tool has been deprecated. For data migration from other databases to Milvus, we recommend that you use the more advanced Milvus-migration Tool.
The Milvus-migration tool currently supprots:
- Elasticsearch to Milvus 2.x
- Faiss to Milvus 2.x
- Milvus 1.x to Milvus 2.x
- Milvus 2.3.x to Milvus 2.3.x or above
We will support migration from more vector data sources such as Pinecone, Chroma, and Qdrant. Stay tuned.
For more information, see the Milvus-migration documentation or its GitHub repository.
--------------------------------- Mivus Data Migration Tool has been deprecated ----------------------
Overview
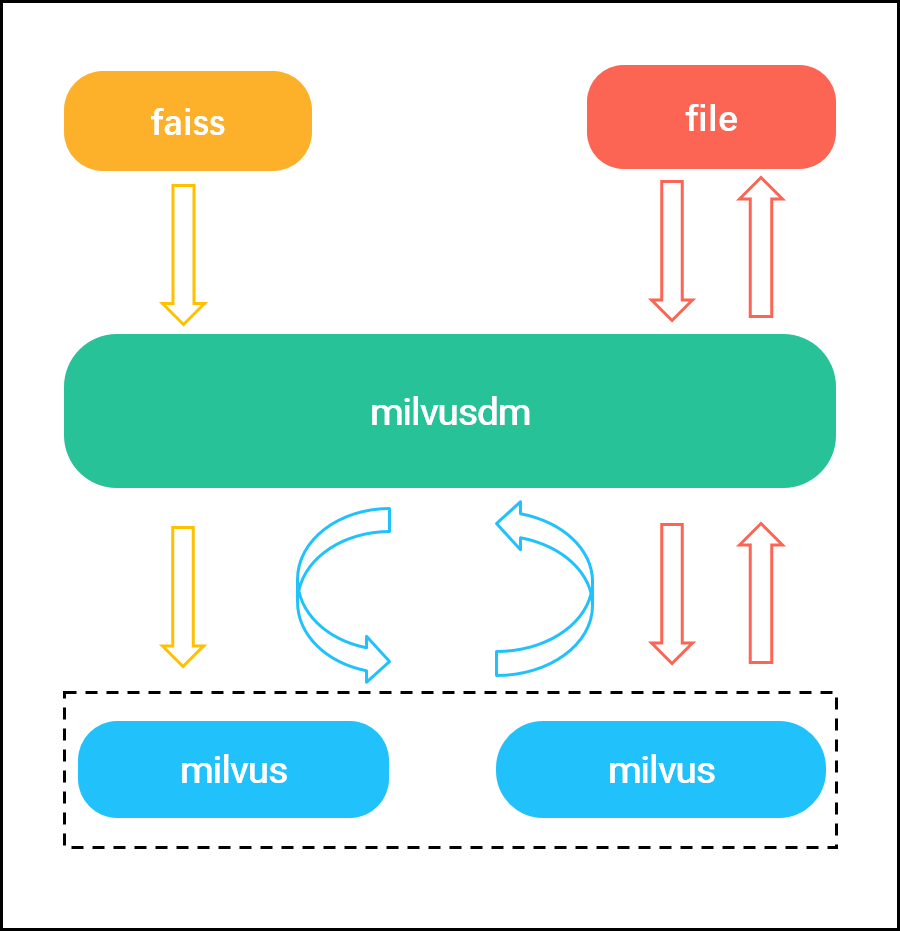
MilvusDM (Milvus Data Migration) is an open-source tool designed specifically for importing and exporting data files with Milvus. MilvusDM can greatly improve data mangement efficiency and reduce DevOps costs in the following ways:
Faiss to Milvus: Import unzipped data from Faiss to Milvus.
HDF5 to Milvus: Import HDF5 files to Milvus.
Milvus to Milvus: Migrate data from a source Milvus to a different target Milvus.
Milvus to HDF5: Save data in Milvus as HDF5 files.
 milvusdm blog 1.png
milvusdm blog 1.png
MilvusDM is hosted on Github and can be easily installed by running the command line pip3 install pymilvusdm. MilvusDM allows you to migrate data in a specific collection or partition. In the following sections, we will explain how to use each data migration type.
Faiss to Milvus
Steps
1.Download F2M.yaml:
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-tools/main/yamls/F2
2.Set the following parameters:
data_path: Data path (vectors and their corresponding IDs) in Faiss.dest_host: Milvus server address.dest_port: Milvus server port.mode: Data can be imported to Milvus using the following modes:Skip: Ignore data if the collection or partition already exists.
Append: Append data if the collection or partition already exists.
Overwrite: Delete data before insertion if the collection or partition already exists.
dest_collection_name: Name of receiving collection for data import.dest_partition_name: Name of receiving partition for data import.collection_parameter: Collection-specific information such as vector dimension, index file size, and distance metric.
F2M:
milvus_version: 1.0.0
data_path: '/home/data/faiss.index'
dest_host: '127.0.0.1'
dest_port: 19530
mode: 'append' # 'skip/append/overwrite'
dest_collection_name: 'test'
dest_partition_name: ''
collection_parameter:
dimension: 256
index_file_size: 1024
metric_type: 'L2'
3.Run F2M.yaml:
$ milvusdm --yaml F2M.yaml
Sample Code
1.Read Faiss files to retrieve vectors and their corresponding IDs.
ids, vectors = faiss_data.read_faiss_data()
2.Insert the retrieved data into Milvus:
insert_milvus.insert_data(vectors, self.dest_collection_name, self.collection_parameter, self.mode, ids, self.dest_partition_name)
HDF5 to Milvus
Steps
1.Download H2M.yaml.
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-tools/main/yamls/H2M.yaml
2.Set the following parameters:
data_path: Path to the HDF5 files.data_dir: Directory holding the HDF5 files.dest_host: Milvus server address.dest_port: Milvus server port.mode: Data can be imported to Milvus using the following modes:Skip: Ignore data if the collection or partition already exists.
Append: Append data if the collection or partition already exists.
Overwrite: Delete data before insertion if the collection or partition already exists.
dest_collection_name: Name of receiving collection for data import.dest_partition_name: Name of receiving partition for data import.collection_parameter: Collection-specific information such as vector dimension, index file size, and distance metric.
Set either
data_pathordata_dir. Do not set both. Usedata_pathto specify multiple file paths, ordata_dirto specify the directory holding your data file.
H2M:
milvus-version: 1.0.0
data_path:
- /Users/zilliz/float_1.h5
- /Users/zilliz/float_2.h5
data_dir:
dest_host: '127.0.0.1'
dest_port: 19530
mode: 'overwrite' # 'skip/append/overwrite'
dest_collection_name: 'test_float'
dest_partition_name: 'partition_1'
collection_parameter:
dimension: 128
index_file_size: 1024
metric_type: 'L2'
3.Run H2M.yaml:
$ milvusdm --yaml H2M.yaml
Sample Code
1.Read the HDF5 files to retrieve vectors and their corresponding IDs:
vectors, ids = self.file.read_hdf5_data()
2.Insert the retrieved data into Milvus:
ids = insert_milvus.insert_data(vectors, self.c_name, self.c_param, self.mode, ids,self.p_name)
Milvus to Milvus
Steps
1.Download M2M.yaml.
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-tools/main/yamls/M2M.yaml
2.Set the following parameters:
source_milvus_path: Source Milvus work path.mysql_parameter: Source Milvus MySQL settings. If MySQL is not used, set mysql_parameter as '’.source_collection: Names of the collection and its partitions in the source Milvus.dest_host: Milvus server address.dest_port: Milvus server port.mode: Data can be imported to Milvus using the following modes:Skip: Ignore data if the collection or partition already exists.
Append: Append data if the collection or partition already exists.
Overwrite: If the collection or partition already exists, delete the data before inserting it.Delete data before insertion if the collection or partition already exists.
M2M:
milvus_version: 1.0.0
source_milvus_path: '/home/user/milvus'
mysql_parameter:
host: '127.0.0.1'
user: 'root'
port: 3306
password: '123456'
database: 'milvus'
source_collection:
test:
- 'partition_1'
- 'partition_2'
dest_host: '127.0.0.1'
dest_port: 19530
mode: 'skip' # 'skip/append/overwrite'
3.Run M2M.yaml.
$ milvusdm --yaml M2M.yaml
Sample Code
1.According to a specified collection or partition’s metadata, read the files under milvus/db on your local drive to retrieve vectors and their corresponding IDs from the source Milvus.
collection_parameter, _ = milvus_meta.get_collection_info(collection_name)
r_vectors, r_ids, r_rows = milvusdb.read_milvus_file(self.milvus_meta, collection_name, partition_tag)
2.Insert the retrieved data into the target Milvus.
milvus_insert.insert_data(r_vectors, collection_name, collection_parameter, self.mode, r_ids, partition_tag)
Milvus to HDF5
Steps
1.Download M2H.yaml:
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-tools/main/yamls/M2H.yaml
2.Set the following parameters:
source_milvus_path: Source Milvus work path.mysql_parameter: Source Milvus MySQL settings. If MySQL is not used, set mysql_parameter as '’.source_collection: Names of the collection and its partitions in the source Milvus.data_dir: Directory for holding the saved HDF5 files.
M2H:
milvus_version: 1.0.0
source_milvus_path: '/home/user/milvus'
mysql_parameter:
host: '127.0.0.1'
user: 'root'
port: 3306
password: '123456'
database: 'milvus'
source_collection: # specify the 'partition_1' and 'partition_2' partitions of the 'test' collection.
test:
- 'partition_1'
- 'partition_2'
data_dir: '/home/user/data'
3.Run M2H.yaml:
$ milvusdm --yaml M2H.yaml
Sample Code
1.According to a specified collection or partition’s metadata, read the files under milvus/db on your local drive to retrieve vectors and their corresponding IDs.
collection_parameter, version = milvus_meta.get_collection_info(collection_name)
r_vectors, r_ids, r_rows = milvusdb.read_milvus_file(self.milvus_meta, collection_name, partition_tag)
2.Save the retrieved data as HDF5 files.
data_save.save_yaml(collection_name, partition_tag, collection_parameter, version, save_hdf5_name)
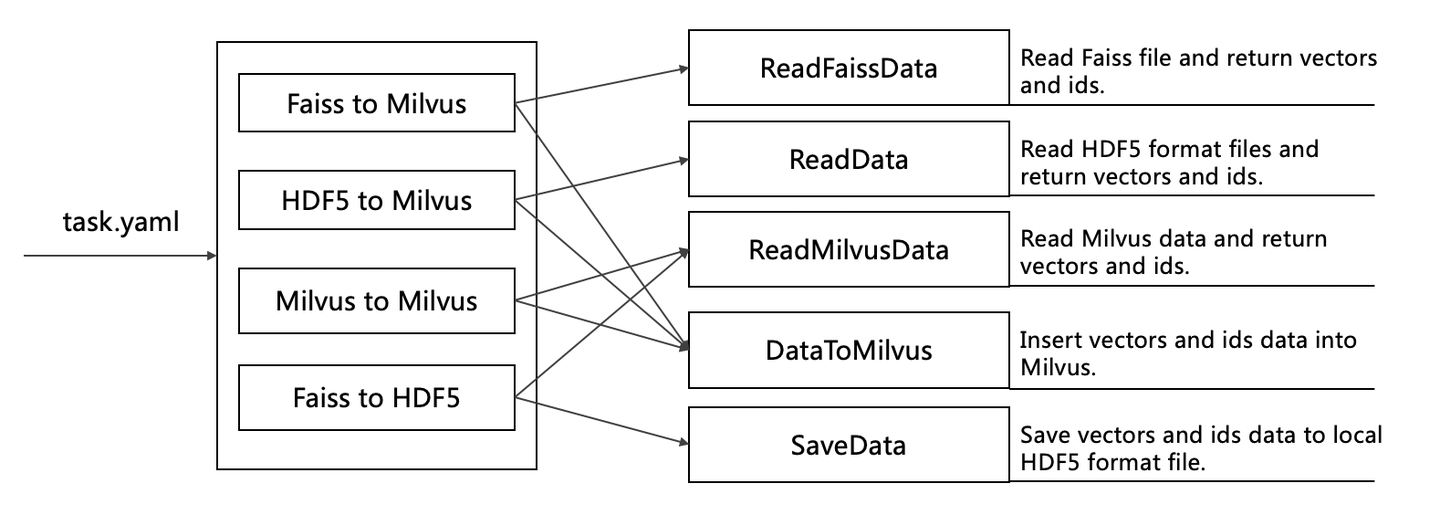
MilvusDM File Structure
The flow chart below shows how MilvusDM performs different tasks according to the YAML file it receives:
 milvusdm blog 2.png
milvusdm blog 2.png
MilvusDM file structure:
pymilvusdm
core
milvus_client.py: Performs client operations in Milvus.
read_data.py: Reads the HDF5 data files on your local drive. (Add your code here to support reading data files in other formats.)
read_faiss_data.py: Reads the data files in Faiss.
read_milvus_data.py: Reads the data files in Milvus.
read_milvus_meta.py: Reads the metadata in Milvus.
data_to_milvus.py: Creates collections or partitions based on parameters in YAML files and imports the vectors and the corresponding vector IDs into Milvus.
save_data.py: Saves the data as HDF5 files.
write_logs.py: Writes logs during runtime.
faiss_to_milvus.py: Imports data from Faiss into Milvus.
hdf5_to_milvus.py: Imports data in HDF5 files into Milvus.
milvus_to_milvus.py: Migrates data from a source Milvus to the target Milvus.
milvus_to_hdf5.py: Exports data in Milvus and saves them as HDF5 files.
main.py: Performs corresponding tasks according to the received YAML file.
setting.py: Configurations relating to running the MilvusDM code.
setup.py: Creates pymilvusdm file packages and uploads them to PyPI (Python Package Index).
Recap
MilvusDM primarily handles migrating data in and out of Milvus, which includes Faiss to Milvus, HDF5 to Milvus, Milvus to Milvus, and Milvus to HDF5.
The following features are planned for upcoming releases:
Import binary data from Faiss to Milvus.
Blocklist and allowlist for data migration between source Milvus and target Milvus.
Merge and import data from multiple colletions or partitions in source Milvus into a new collection in target Milvus.
Backup and recovery of the Milvus data.
The MilvusDM project is open sourced on Github. Any and all contributions to the project are welcome. Give it a star 🌟, and feel free to file an issue or submit your own code!
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word