Hands-on Tutorial: Build a RAG-Powered Document Assistant in 10 Minutes with Dify and Milvus

What if you could turn your entire documentation library—thousands of pages of technical specs, internal wikis, and code documentation—into an intelligent AI assistant that instantly answers specific questions?
Even better, what if you could build it in less time than it takes to fix a merge conflict?
That’s the promise of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) when implemented the right way.
While ChatGPT and other LLMs are impressive, they quickly hit their limits when asked about your company’s specific documentation, codebase, or knowledge base. RAG bridges this gap by integrating your proprietary data into the conversation, providing you with AI capabilities that are directly relevant to your work.
The problem? Traditional RAG implementation looks like this:
Write custom embedding generation pipelines
Configure and deploy a vector database
Engineer complex prompt templates
Build retrieval logic and similarity thresholds
Create a usable interface
But what if you could skip straight to the results?
In this tutorial, we’ll build a simple RAG application using two developer-focused tools:
Dify: An open-source platform that handles the RAG orchestration with minimal configuration
Milvus: A blazing-fast open-source vector database purpose-built for similarity search and AI searches
By the end of this 10-minute guide, you’ll have a working AI assistant that can answer detailed questions about any document collection you throw at it - no machine learning degree required.
What You’ll Build
In just a few minutes of active work, you’ll create:
A document processing pipeline that converts any PDF into queryable knowledge
A vector search system that finds exactly the right information
A chatbot interface that answers technical questions with pinpoint accuracy
A deployable solution you can integrate with your existing tools
The best part? Most of it is configured through a simple user interface (UI) instead of custom code.
What You’ll Need
Basic Docker knowledge (just
docker-compose up -dlevel)An OpenAI API key
A PDF document to experiment with (we’ll use a research paper)
Ready to build something actually useful in record time? Let’s get started!
Building Your RAG Application with Milvus and Dify
In this section, we will build a simple RAG app with Dify, where we can ask questions about the information contained in a research paper. For the research paper, you can use any paper you want; however, in this case, we will use the famous paper that introduced us to the Transformer architecture, "Attention is All You Need."
We will use Milvus as our vector storage, where we will store all the necessary contexts. For the embedding model and the LLM, we’ll use models from OpenAI. Therefore, we need to set up an OpenAI API key first. You can learn more about setting it up here.
Step 1: Starting Dify and Milvus Containers
In this example, we’ll self-host Dify with Docker Compose. Therefore, before we begin, ensure that Docker is installed on your local machine. If you haven’t, install Docker by referring to its installation page.
Once we have Docker installed, we need to clone the Dify source code into our local machine with the following command:
git clone <<https://github.com/langgenius/dify.git>>
Next, go to the docker directory inside of the source code that you’ve just cloned. There, you need to copy the .env file with the following command:
cd dify/docker
cp .env.example .env
In a nutshell, .env file contains the configurations needed to set your Dify app up and running, such as the selection of vector databases, the credentials necessary to access your vector database, the address of your Dify app, etc.
Since we’re going to use Milvus as our vector database, then we need to change the value of VECTOR_STORE variable inside .env file to milvus. Also, we need to change the MILVUS_URI variable to http://host.docker.internal:19530 to ensure that there’s no communication issue between Docker containers later on after deployment.
VECTOR_STORE=milvus
MILVUS_URI=http://host.docker.internal:19530
Now we are ready to start the Docker containers. To do so, all we need to do is to run the docker compose up -d command. After it finishes, you’ll see similar output in your terminal as below:
docker compose up -d
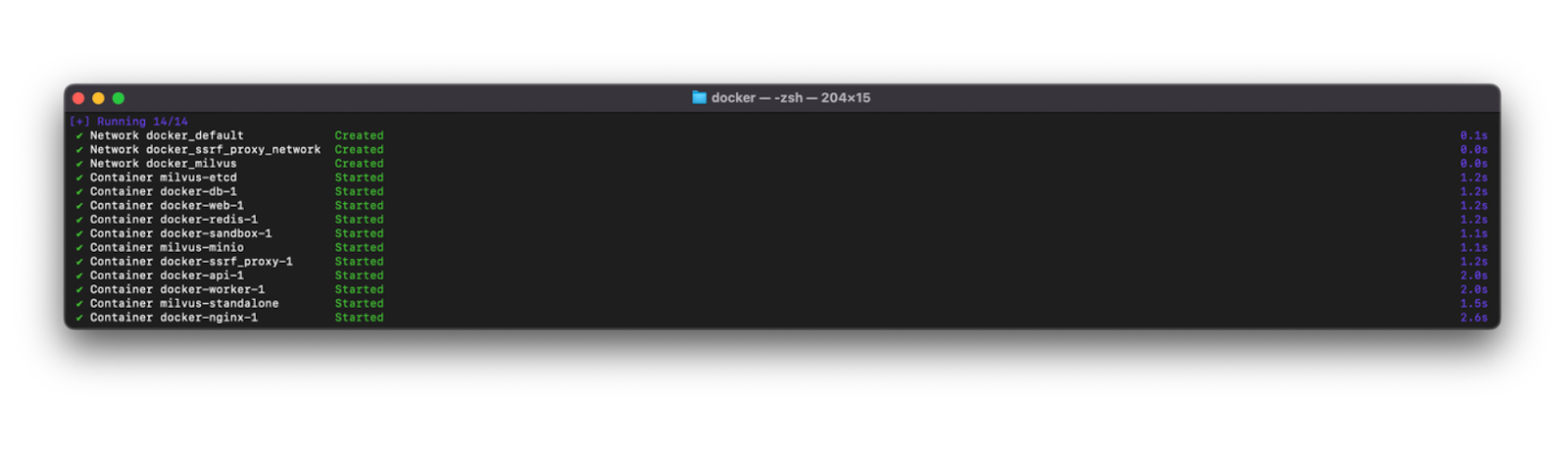
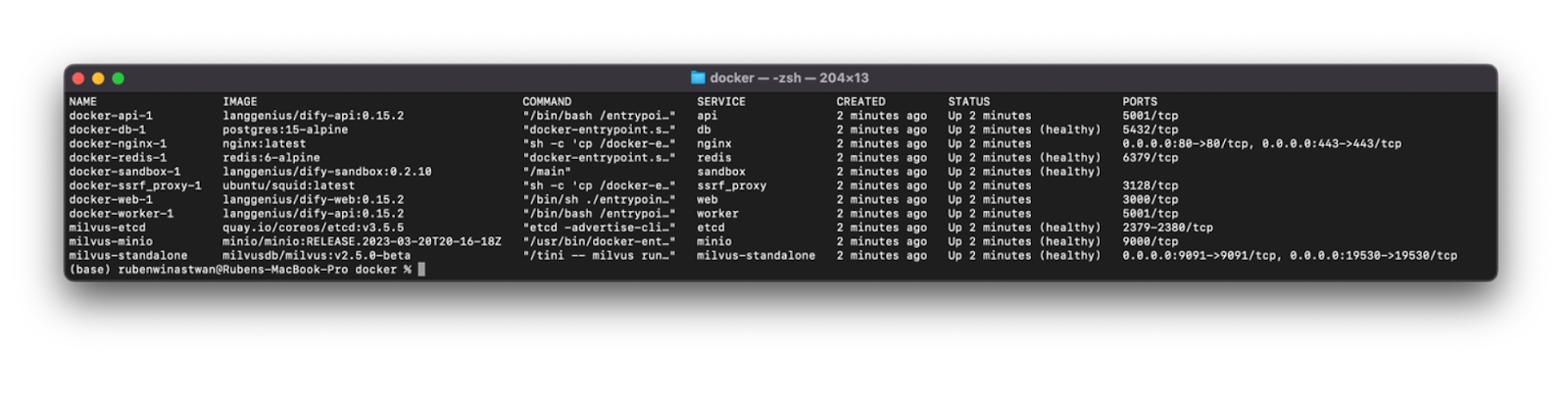
We can check the status of all containers and see if they’re up and running healthily with docker compose ps command. If they’re all healthy, you’ll see an output as below:
docker compose ps
And finally, if we head up to http://localhost/install, you’ll see a Dify landing page where we can sign up and start building our RAG application in no time.
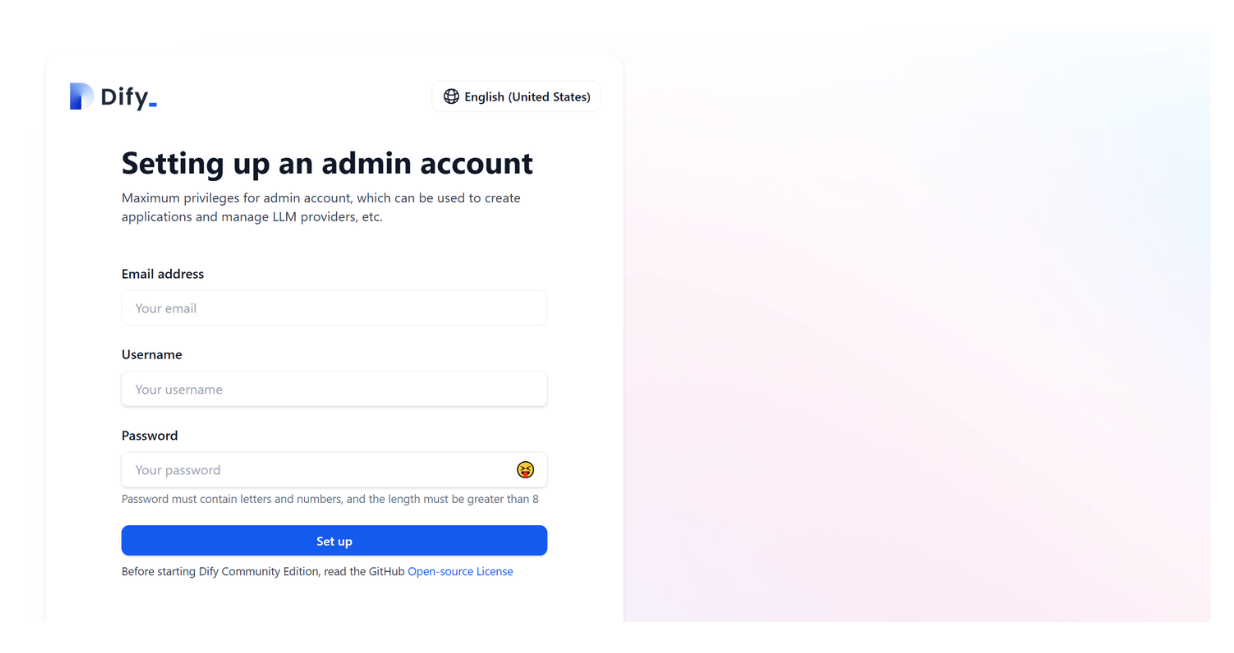
Once you’ve signed up, then you can just log into Dify with your credentials.
Step 2: Setting Up OpenAI API Key
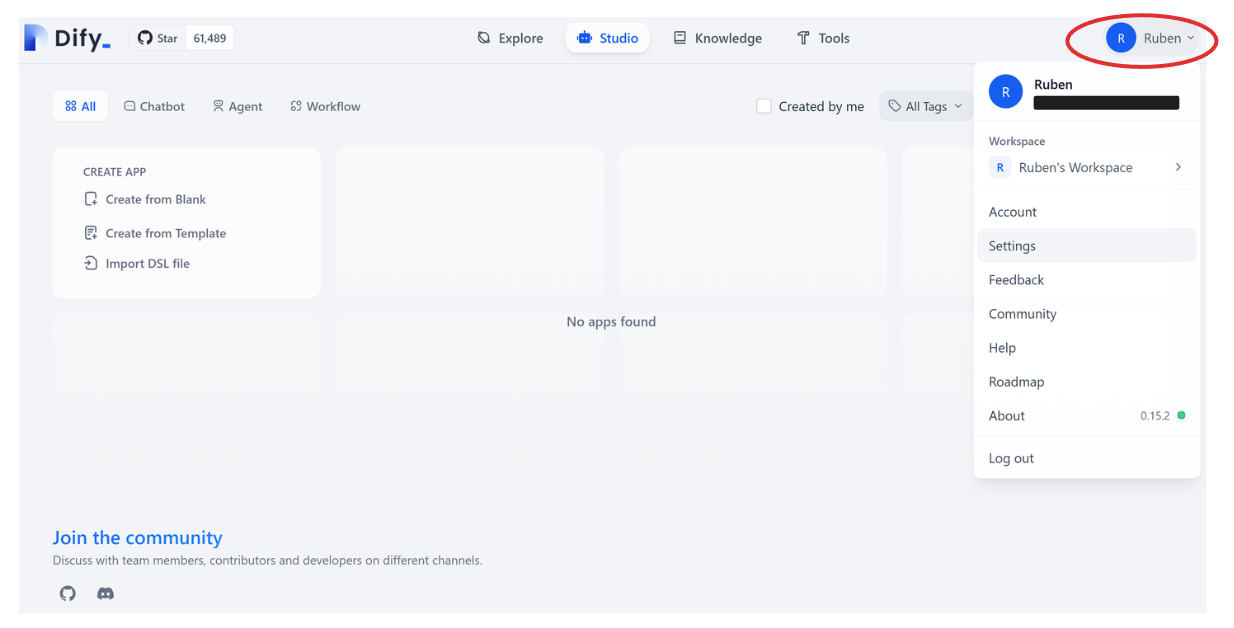
The first thing we need to do after signing up for Dify is to set up our API keys that we’ll use to call the embedding model as well as the LLM. Since we’re going to use models from OpenAI, we need to insert our OpenAI API key into our profile. To do so, go to “Settings” by hovering your cursor over your profile on the top right of the UI, as you can see in the screenshot below:
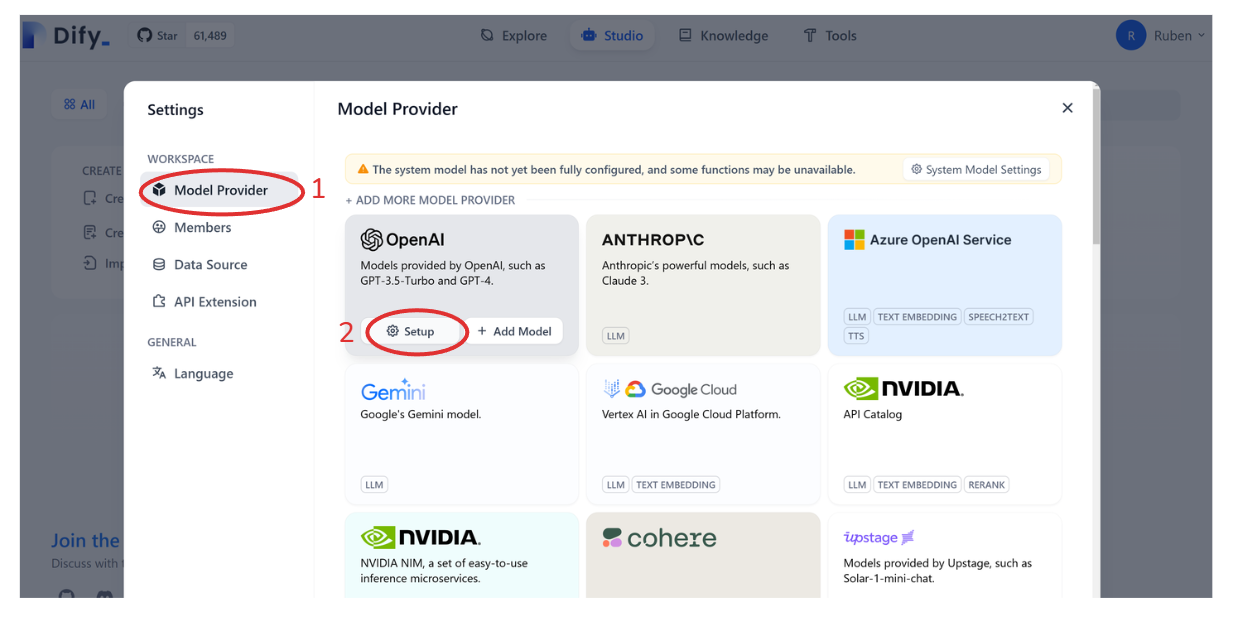
Next, go to “Model Provider,” hover your cursor on OpenAI, and then click “Setup.” You’ll then see a pop-up screen where you’re prompted to enter your OpenAI API key. Once we’re done, we’re ready to use models from OpenAI as our embedding model and LLM.
Step 3: Inserting Documents into Knowledge Base
Now let’s store the knowledge base for our RAG app. The knowledge base consists of a collection of internal documents or texts that can be used as relevant contexts to help the LLM generates more accurate responses.
In our use case, our knowledge base is essentially the “Attention is All You Need” paper. However, we can’t store the paper as it is due to multiple reasons. First, the paper is too long, and giving an overly long context to the LLM wouldn’t help as the context is too broad. Second, we can’t perform similarity searches to fetch the most relevant context if our input is raw text.
Therefore, there are at least two steps we need to take before storing our paper into the knowledge base. First, we need to divide the paper into text chunks, and then transform each chunk into an embedding via an embedding model. Finally, we can store these embeddings into Milvus as our vector database.
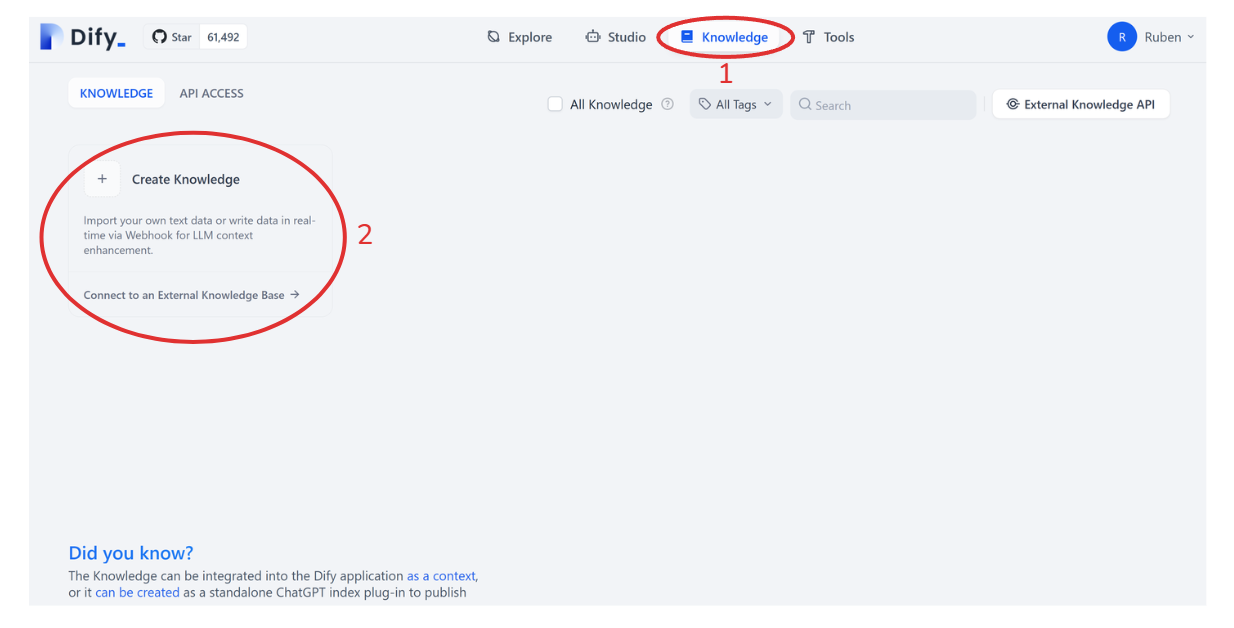
Dify makes it easy for us to split the texts in the paper into chunks and turn them into embeddings. All we need to do is upload the PDF file of the paper, set the chunk length, and choose the embedding model via a slider. To do all these steps, go to “Knowledge” and then click "Create Knowledge". Next, you’ll be prompted to upload the PDF file from your local computer. Therefore, it’s better if you download the paper from ArXiv and save it on your computer first.
Once we’ve uploaded the file, we can set the chunk length, indexing method, the embedding model we want to use, and retrieval settings.
In the “Chunk Setting” area, you can choose any number as the maximum chunk length (in our use case, we’ll set it to 100). Next, for “Index Method,” we need to choose the “High Quality” option as it’ll enable us to perform similarity searches to find relevant contexts. For “Embedding Model,” you can choose any embedding model from OpenAI you want, but in this example, we’re going to use the text-embedding-3-small model. Lastly, for “Retrieval Setting,” we need to choose “Vector Search” as we want to perform similarity searches to find the most relevant contexts.
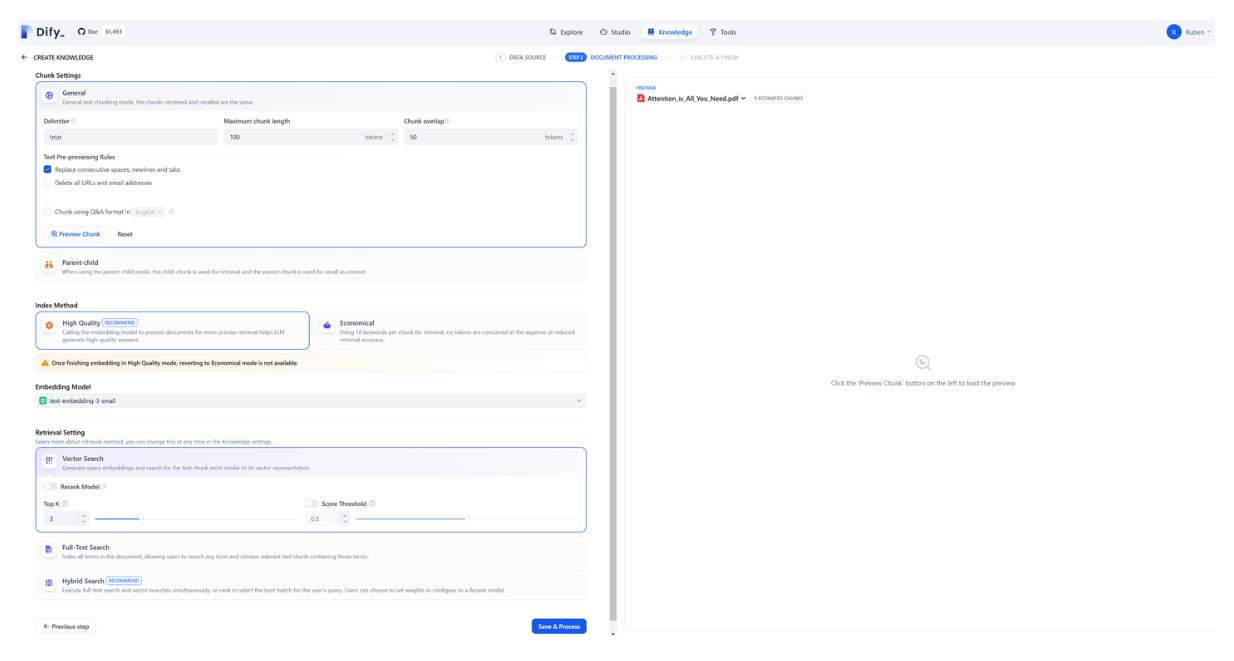
Now if you click on “Save & Process” and everything goes well, you’ll see a green tick appear as shown in the following screenshot:
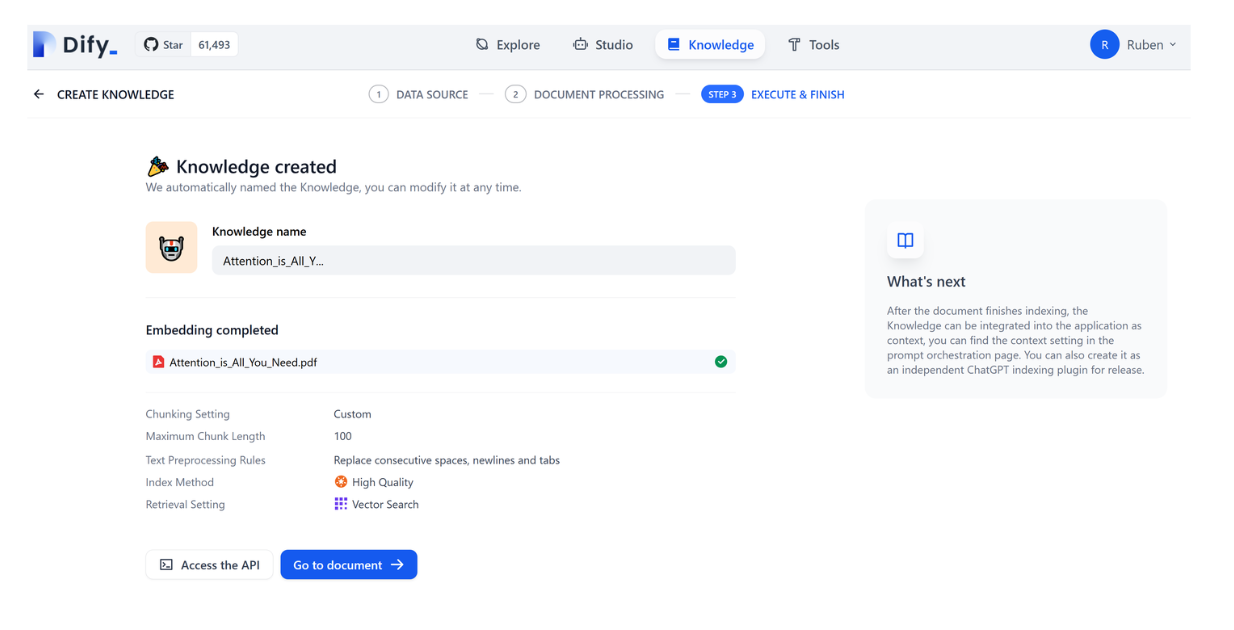
Step 4: Creating the RAG App
Up until this point, we have successfully created a knowledge base and stored it inside our Milvus database. Now we’re ready to create the RAG app.
Creating the RAG app with Dify is very straightforward. We need to go to “Studio” instead of “Knowledge” like before, and then click on “Create from Blank.” Next, choose “Chatbot” as the app type and give your App a name inside the provided field. Once you’re done, click “Create.” Now you’ll see the following page:
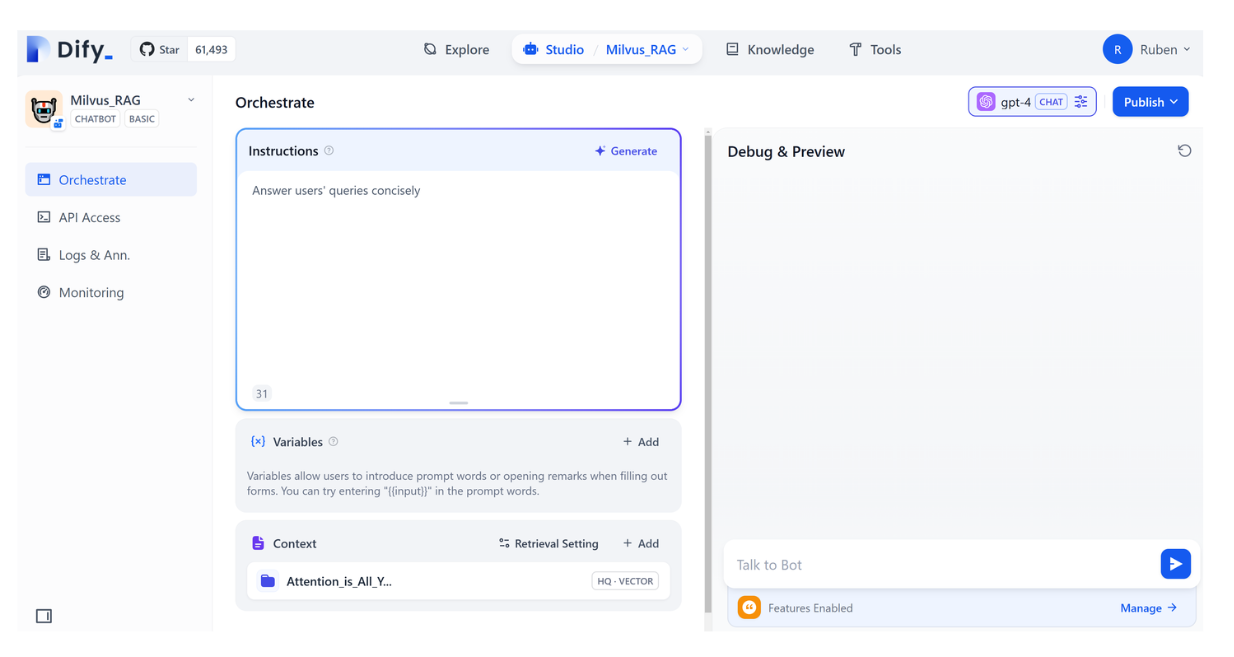
Under the “Instruction” field, we can write a system prompt such as “Answer the query from the user concisely.” Next, as “Context,” we need to click on the “Add” symbol, and then add the knowledge base that we’ve just created. This way, our RAG app will fetch possible contexts from this knowledge base to answer the user’s query.
Now that we’ve added the knowledge base to our RAG app, the last thing we need to do is choose the LLM from OpenAI. To do so, you can click on the model list available in the upper right corner, as you can see in the screenshot below:
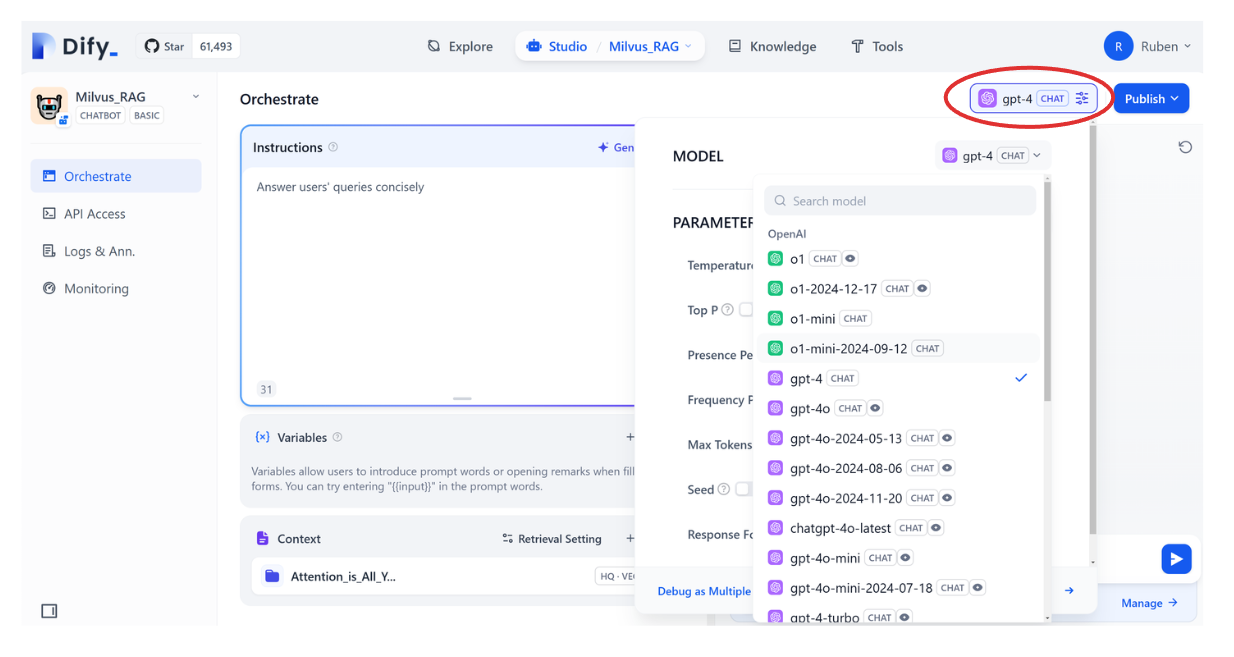
And now we’re ready to publish our RAG application! In the upper right-hand corner, click “Publish,” and there you can find many ways to publish our RAG app: we can simply run it in a browser, embed it on our website, or access the app via API. In this example, we’ll just run our app in a browser, so we can click on "Run App".
And that’s it! Now you can ask the LLM anything related to the “Attention is All You Need” paper or any documents included in our knowledge base.
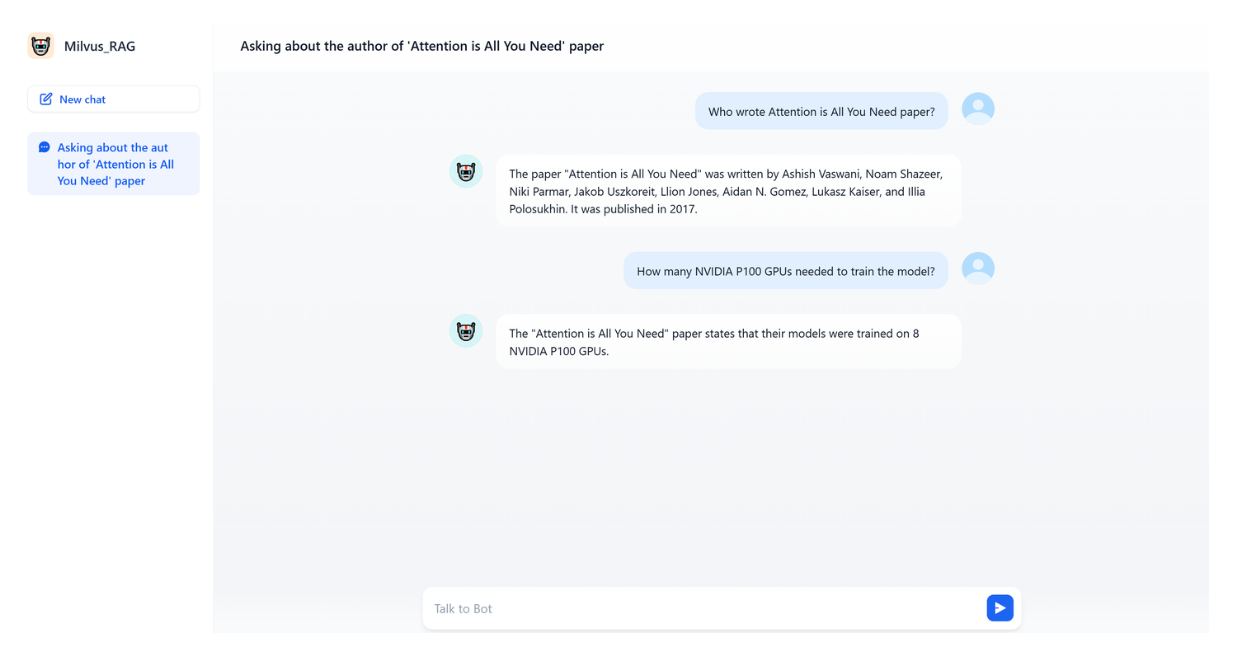
Conclusion
You’ve now built a working RAG application using Dify and Milvus, with minimal code and configuration. This approach makes the complex RAG architecture accessible to developers without requiring deep expertise in vector databases or LLM integration. Key takeaways:
- Low setup overhead: Using Docker Compose simplifies deployment
- No-code/low-code orchestration: Dify handles most of the RAG pipeline
- Production-ready vector database: Milvus provides efficient embedding storage and retrieval
- Extensible architecture: Easy to add documents or adjust parameters For production deployment, consider:
- Setting up authentication for your application
- Configuring proper scaling for Milvus (especially for larger document collections)
- Implementing monitoring for your Dify and Milvus instances
- Fine-tuning retrieval parameters for optimal performance The combination of Dify and Milvus enables the rapid development of RAG applications that can effectively leverage your organization’s internal knowledge with modern large language models (LLMs). Happy building!
Additional Resources
- What You'll Build
- What You'll Need
- Building Your RAG Application with Milvus and Dify
- Step 1: Starting Dify and Milvus Containers
- Step 2: Setting Up OpenAI API Key
- Step 3: Inserting Documents into Knowledge Base
- Step 4: Creating the RAG App
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word