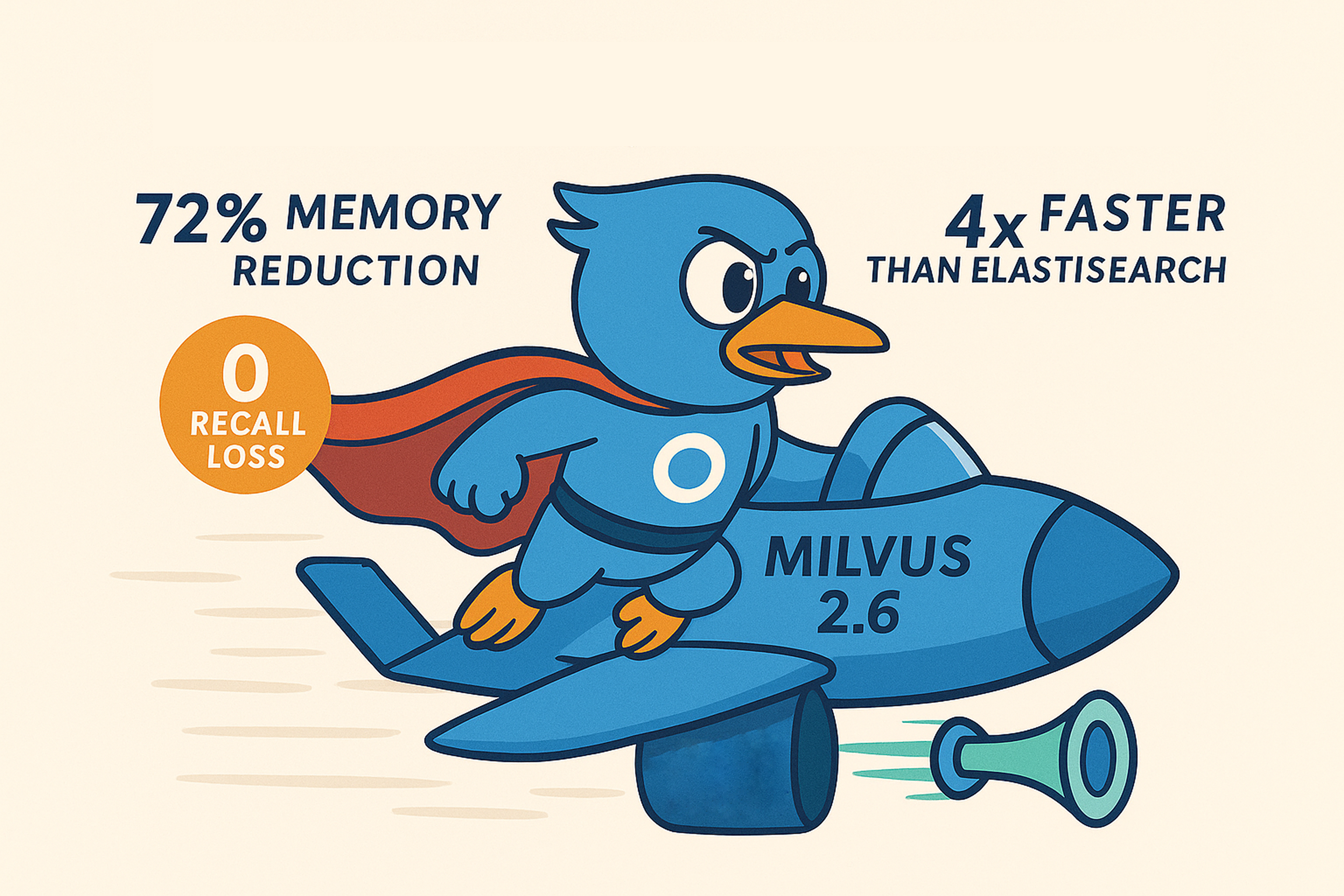
Milvus 2.6 Preview: 72% Memory Reduction Without Compromising Recall and 4x Faster Than Elasticsearch
Throughout this week, we’ve shared a range of exciting innovations in Milvus that push the boundaries of vector database technology:
Vector Search in the Real World: How to Filter Efficiently Without Killing Recall
Bring Vector Compression to the Extreme: How Milvus Serves 3× More Queries with RaBitQ
MinHash LSH in Milvus: The Secret Weapon for Fighting Duplicates in LLM Training Data
Now, as we wrap up our Milvus Week series, I’m excited to give you a sneak peek of what’s coming in Milvus 2.6—a crucial milestone in our 2025 product roadmap that’s currently in development, and how these improvements will transform AI-powered search. This upcoming release brings together all these innovations and more across three critical fronts: cost-efficiency optimization, advanced search capabilities, and a new architecture that pushes vector search beyond 10 billion vector scale.
Let’s dive into some of the key improvements you can expect when Milvus 2.6 arrives this June, starting with what might be the most immediately impactful: dramatic reductions in memory usage and cost, and ultra-fast performance.
Cost-Reduction: Slash Memory Usage While Boosting Performance
Relying on expensive memory presents one of the biggest obstacles to scaling vector search to billions of records. Milvus 2.6 will introduce several key optimizations that dramatically lower your infrastructure costs while improving performance.
RaBitQ 1-bit Quantization: 72% Memory Reduction with 4× QPS and No Recall Loss
Memory consumption has long been the Achilles’ heel of large-scale vector databases. While vector quantization isn’t new, most existing approaches sacrifice too much search quality for memory savings. Milvus 2.6 will tackle this challenge head-on by introducing RaBitQ 1-bit quantization in production environments.
What makes our implementation special is the adjustable Refine optimization capability we’re building. By implementing a primary index with RaBitQ quantization plus SQ4/SQ6/SQ8 Refine options, we’ve achieved an optimal balance between memory usage and search quality (~95% recall).
Our preliminary benchmarks reveal promising results:
| Performance Metric | Traditional IVF_FLAT | RaBitQ (1-bit) Only | RaBitQ (1-bit) + SQ8 Refine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Footprint | 100% (baseline) | 3% (97% reduction) | 28% (72% reduction) |
| Recall Quality | 95.2% | 76.3% | 94.9% |
| Query Throughput (QPS) | 236 | 648 (2.7× faster) | 946 (4× faster) |
Table: VectorDBBench evaluation with 1M vectors of 768 dimensions, tested on AWS m6id.2xlarge
The real breakthrough here isn’t just the memory reduction, but achieving this while simultaneously delivering a 4× throughput improvement without compromising accuracy. This means you’ll be able to serve the same workload with 75% fewer servers or handle 4× more traffic on your existing infrastructure.
For enterprise users using fully managed Milvus on Zilliz Cloud, we’re developing automated configuration profiles that will dynamically adjust RaBitQ parameters based on your specific workload characteristics and precision requirements.
400% Faster Full-text Search Than Elasticsearch
Full-text search capabilities in vector databases have become essential for building hybrid retrieval systems. Since introducing BM25 in Milvus 2.5, we’ve received enthusiastic feedback—along with requests for better performance at scale.
Milvus 2.6 will deliver substantial performance gains on BM25. Our testing on the BEIR dataset shows 3-4× higher throughput than Elasticsearch with equivalent recall rates. For some workloads, the improvement reaches up to 7× higher QPS.
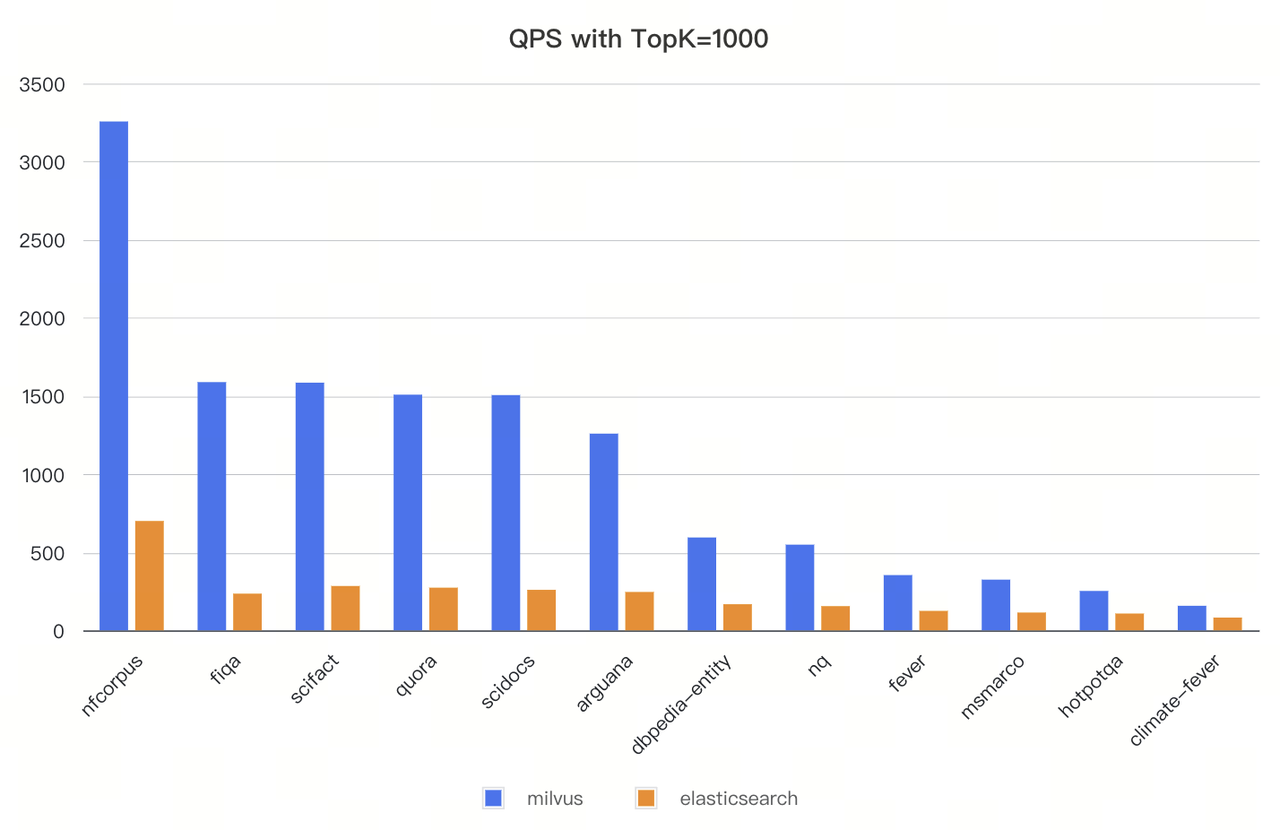
Figure: Milvus vs. Elasticsearch on throughput
JSON Path Index: 99% Lower Latency for Complex Filtering
Modern AI applications rarely rely on vector similarity alone—they almost always combine vector search with metadata filtering. As these filtering conditions become more complex (especially with nested JSON objects), query performance can deteriorate rapidly.
Milvus 2.6 will introduce a targeted indexing mechanism for nested JSON paths that allows you to create indexes on specific paths (e.g., $meta user_info.location) within JSON fields. Instead of scanning entire objects, Milvus will directly look up values from pre-built indexes.
In our evaluation with 100 M+ records, JSON Path Index reduced filter latency from 140ms (P99: 480ms) to just 1.5ms (P99: 10ms)—a 99% reduction that will transform previously impractical queries into instant responses.
This feature will be particularly valuable for:
Recommendation systems with complex user attribute filtering
RAG applications that filter documents by various labels
Next-Generation Search: From Basic Vector Similarity to Production-Grade Retrieval
Vector search alone isn’t enough for modern AI applications. Users demand the precision of traditional information retrieval combined with the semantic understanding of vector embeddings. Milvus 2.6 will introduce several advanced search features that bridge this gap.
Better Full-text Search with Multi-language Analyzer
Full-text search is highly language-dependent… Milvus 2.6 will introduce a completely revamped text analysis pipeline with multi-language support:
RUN_ANALYZERsyntax support for analyzer/tokenization configuration observabilityLindera tokenizer for Asian languages like Japanese and Korean
ICU tokenizer for comprehensive multilingual support
Granular language configuration for defining language-specific tokenization rules
Enhanced Jieba with support for custom dictionary integration
Expanded filter options for more precise text processing
For global applications, this means better multilingual search without specialized per-language indexing or complex workarounds.
Phrase Match: Capturing Semantic Nuance in Word Order
Word order conveys critical meaning distinctions that keyword search often misses. Try comparing “machine learning techniques” with "learning machine techniques"—same words, totally different meaning.
Milvus 2.6 will add Phrase Match, giving users more control over word order and proximity than full-text search or exact string match:
PHRASE_MATCH(field_name, phrase, slop)
The slop parameter will provide flexible control over word proximity—0 requires exact consecutive matches, while higher values allow for minor variations in phrasing.
This feature will be particularly valuable for:
Legal document search where exact phrasing carries legal significance
Technical content retrieval where term order distinguishes different concepts
Patent databases where specific technical phrases must be matched precisely
Time-Aware Decay Functions: Automatically Prioritize Fresh Content
Information value often diminishes with time. News articles, product releases, and social posts all become less relevant as they age, yet traditional search algorithms treat all content equally, regardless of timestamp.
Milvus 2.6 will introduce Decay Functions for time-aware ranking that automatically adjust relevance scores based on document age.
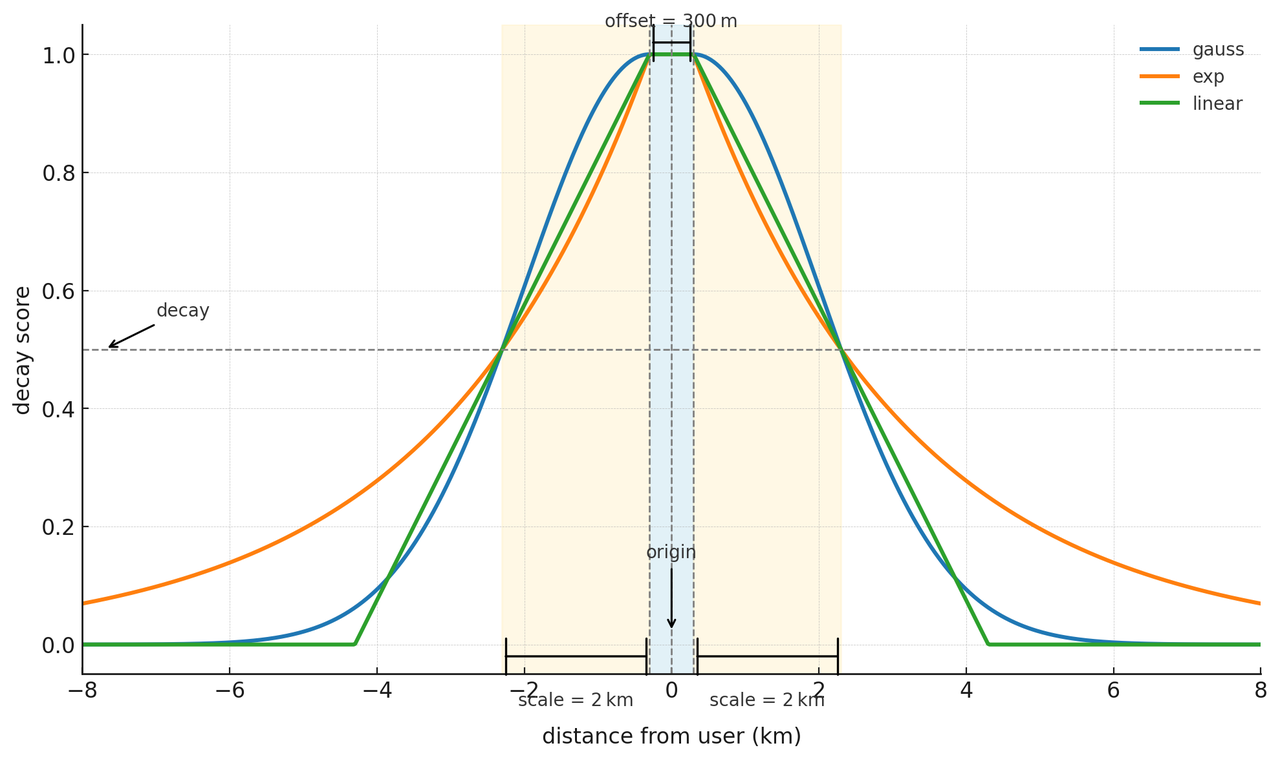
You’ll be able to configure:
Function type: Exponential (rapid decay), Gaussian (gradual decay), or Linear (constant decay)
Decay rate: How quickly relevance diminishes over time
Origin point: The reference timestamp for measuring time differences
This time-sensitive re-ranking will ensure that the most up-to-date and contextually relevant results appear first, which is crucial for news recommendation systems, e-commerce platforms, and social media feeds.
Data in, Data Out: From Raw Text to Vector Search in One Step
One of the biggest developer pain points with vector databases has been the disconnect between raw data and vector embeddings. Milvus 2.6 will dramatically simplify this workflow with a new Function interface that integrates third-party embedding models directly into your data pipeline. This streamlines your vector search pipeline with one single call.
Instead of pre-computing embeddings, you’ll be able to:
Insert raw data directly: Submit text, images, or other content to Milvus
Configure embedding providers for vectorization: Milvus can connect to embedding model services like OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, Google Vertex AI, and Hugging Face.
Query using natural language: Search using text queries, not vector embeddings
This will create a streamlined “Data-In, Data-Out” experience where Milvus handles the vector generation internally, making your application code more straightforward.
Architectural Evolution: Scaling to Hundreds of Billions of Vectors
A good database doesn’t just have great features, it must also deliver those features at scale, battle-tested in production.
Milvus 2.6 will introduce a fundamental architectural change that enables cost-effective scaling to hundreds of billions of vectors. The highlight is a new hot-cold tiered storage architecture that intelligently manages data placement based on access patterns, automatically moving hot data to high-performance memory/SSD while placing cold data in more economical object storage. This approach can dramatically reduce costs while maintaining query performance where it matters most.
Additionally, a new Streaming Node will enable real-time vector processing with direct integration to streaming platforms like Kafka and Pulsar and the newly created Woodpecker, making new data searchable immediately without batch delays.
Stay tuned for Milvus 2.6
Milvus 2.6 is currently in active development and will be available this June. We’re excited to bring you these breakthrough performance optimizations, advanced search capabilities, and a new architecture to help you build scalable AI applications at lower cost.
In the meantime, we welcome your feedback on these upcoming features. What excites you most? Which capabilities would have the most impact on your applications? Join the conversation in our Discord channel or follow our progress on GitHub.
Want to be the first to know when Milvus 2.6 is released? Follow us on LinkedIn or X for the latest updates.
- Cost-Reduction: Slash Memory Usage While Boosting Performance
- RaBitQ 1-bit Quantization: 72% Memory Reduction with 4× QPS and No Recall Loss
- 400% Faster Full-text Search Than Elasticsearch
- JSON Path Index: 99% Lower Latency for Complex Filtering
- Next-Generation Search: From Basic Vector Similarity to Production-Grade Retrieval
- Better Full-text Search with Multi-language Analyzer
- Phrase Match: Capturing Semantic Nuance in Word Order
- Time-Aware Decay Functions: Automatically Prioritize Fresh Content
- Data in, Data Out: From Raw Text to Vector Search in One Step
- Architectural Evolution: Scaling to Hundreds of Billions of Vectors
- Stay tuned for Milvus 2.6
On This Page
Try Managed Milvus for Free
Zilliz Cloud is hassle-free, powered by Milvus and 10x faster.
Get StartedLike the article? Spread the word